Breast Reconstruction with Breast Implants
Breast Reconstruction with Breast Implants
Breast reconstruction using breast implants is one of a number of different plastic surgery techniques that can be used to reconstruct a breast. Breast implants can be used to help recreate a breast removed by mastectomy, or to add volume to a breast significantly reduced in size following lumpectomy.
Of all of the techniques of breast reconstruction, reconstruction using breast implants generally requires the shortest hospital stay—often just overnight. In addition, when implants are used for reconstruction, scars can be limited to just the breast or breasts. For these and other reasons, breast reconstruction using breast implants, for many women, is the preferred approach to breast restoration, especially if they are able to have a one-stage implant reconstruction and avoid tissue expansion.
Reconstruction with breast implants is sometimes described as being “simple,” “straightforward” and/or the “least invasive” method of breast reconstruction. In some ways, these descriptions are accurate, however, they reflect a somewhat narrow view of what breast reconstruction means for each person. While an implant breast reconstruction may involve less initial surgery than a natural-tissue reconstruction, women who chose to have implant reconstructions have much higher rates of unplanned reoperations and reconstruction failures than do those who chose natural-tissue reconstructions.
Of course, since each method of breast reconstruction has specific advantages and disadvantages, the best procedure for your reconstruction will depend on many factors including your medical history, your breast cancer treatment plan, and most importantly, your personal preference and goals. The advantages of breast implant reconstruction should be weighed against the disadvantages, including a high rate of unplanned re-operation and the anticipated lifespan of breast implants. For women who wish to undergo restorative breast surgery without an implant, natural-tissue reconstructive procedures may be appealing.
Advantages of Breast Implant Reconstruction
The advantages of implant breast reconstruction over natural-tissue breast reconstruction include:
- Limiting your healing and surgical scars to the breast area alone
- Shorter initial surgery and hospital stay
- Slightly shorter initial recovery time
Implant breast reconstruction may be a good option if:
- You want to avoid having a scar on another part of the body.
- You want to have breast reconstruction with the shortest possible recovery time.
- You want to achieve a breast size that is larger than possible even with the latest “stacked” flap natural-tissue reconstruction options.
- You will not have or have not had radiation therapy. (Radiation therapy significantly increases the chances of developing significant problems with an implant reconstruction.)
- You are not healthy enough to undergo a natural-tissue reconstruction procedure.
Breast Implant Reconstruction Techniques
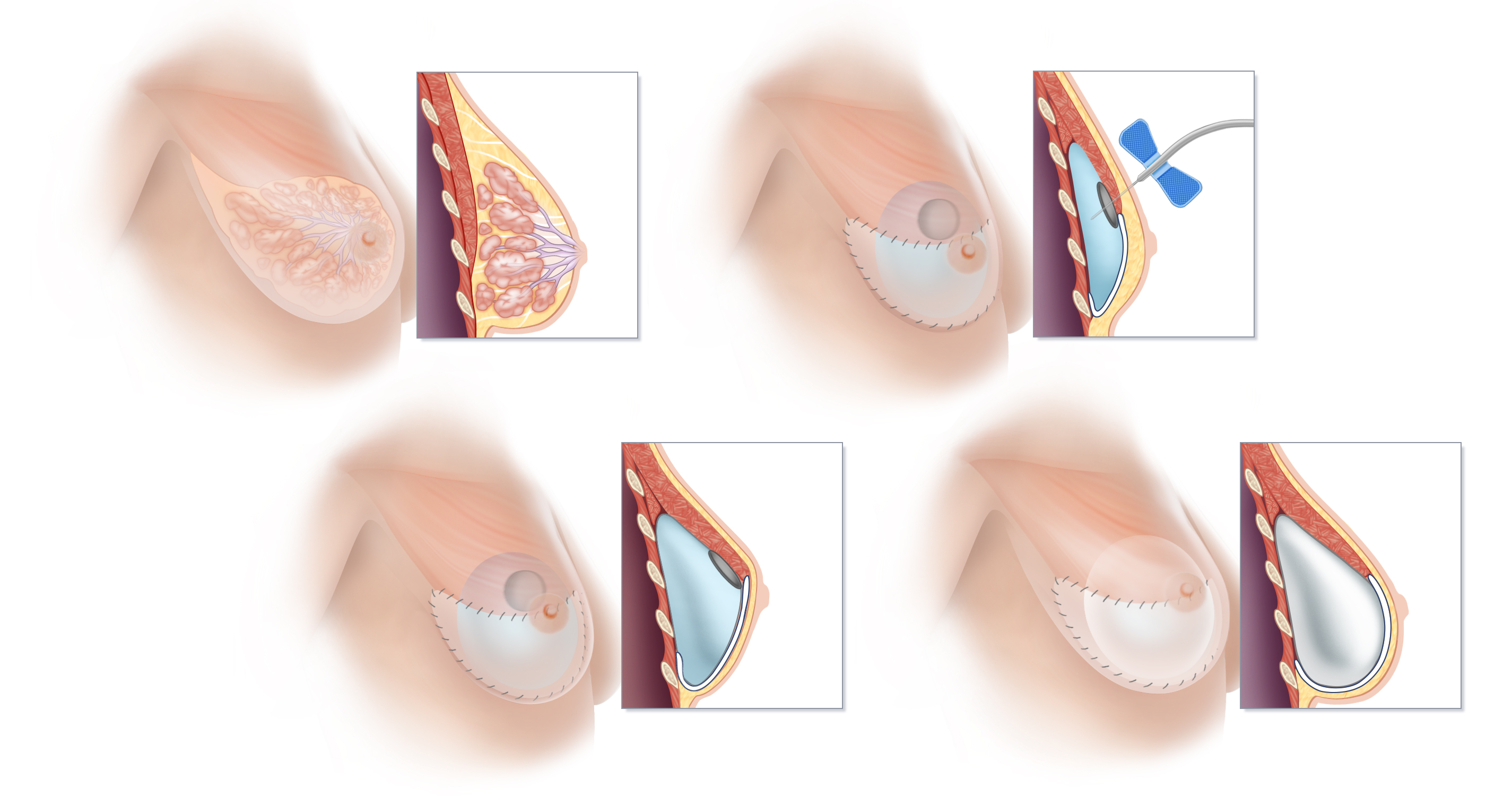
One-Step Prepectoral Implant Breast Reconstruction
In certain situations, a breast implant can be placed directly into the space created by mastectomy. This state-of-the-art approach, known as pre-pectoral implant reconstruction, allows some women to skip the tissue expansion process. When done in combination with nipple-preserving mastectomy, a breast can sometimes be fully reconstructed in a single surgical procedure.
To learn more about one-stage breast implant reconstruction, click here
The current state-of-the-art approach to reconstruction using breast implants avoids damage to the pectoralis muscle that necessarily occurs with traditional tissue expander-implant breast reconstruction techniques. (A) Breast tissue is normally located just in front of the pectoralis muscle of the chest. (B) When breast tissue is removed by mastectomy, an empty space is inherently created between the pectoralis muscle and the breast skin. Prepectoral breast implant reconstruction takes advantage of this empty space. (C) Placing a silicone-filled implant wrapped in specialized acellular dermal matrix directly into the space that results at the time of mastectomy avoids the weakness and discomfort commonly reported with traditional breast implant reconstructions. The normal anatomy and function of the pectoralis muscle is preserved, and visible movement of the implant with muscle contraction—a phenomenon known as “animation deformity”—which occurs frequently with traditional under-the-muscle reconstruction, is avoided.

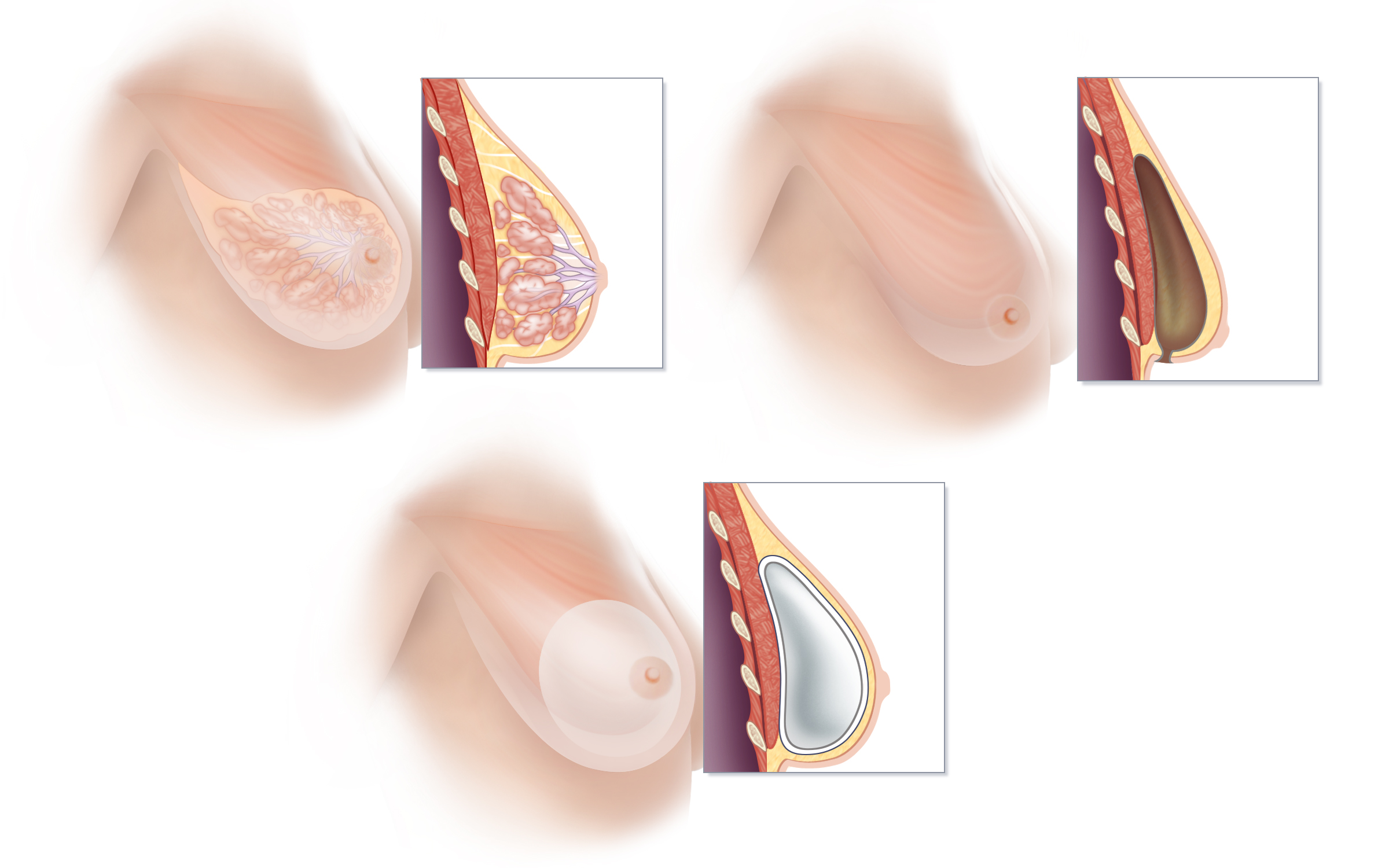
Tissue Expander/Implant Breast Reconstruction
Traditional implant reconstruction involves two or three surgical procedures, beginning, at the time of mastectomy, with the placement of a “tissue expander” under one of the muscles of the chest. The tissue expander is gradually inflated by adding air or fluid to the device over a period of weeks to months. At a second surgery, the tissue expander is removed, and a breast implant is placed.
To learn more about tissue expander/implant reconstruction, click here
(A) Breast tissue is located on top of the muscles of the chest, between the pectoralis muscle and the skin. The lobules of the breast responsible for milk production drain into a system of ducts that travel to the nipple. If a woman’s reconstructive plan calls for a breast implant to be placed “under the muscle,” the pectoralis muscle must be stretched out to create ample space for the implant. In order to create this space, the lower edge of the pectoralis major is surgically separated from the chest wall, and a tissue expander is inserted beneath this muscle. The lower portion of the tissue expander is then typically covered with a specialized acellular dermal matrix to provided added support. (B) At each of a series of office visits following recovery from surgery, the tissue expander is gradually inflated by injection with sterile fluid or air. (C) Once the tissue expander is fully expanded and sufficient space created, an additional surgical procedure is scheduled to remove the expander and replace it with a breast implant. (D) Below the stretched-out pectoralis muscle, a breast implant has replaced the tissue expander. In many cases, the stretched muscle will cover only the upper portion of the implant, and more complete coverage of the breast implant is accomplished by using a tissue matrix such as AlloDerm or Dermacell® between the lower edge of the pectoralis muscle and the chest wall.

Breast Implant Breast Reconstruction in New York and Connecticut
Contact us to schedule a consultation, or if you would like more information about the options for breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Our practice has offices in Greenwich, Connecticut and New York. We perform breast reconstruction surgery at several hospitals in Connecticut and New York.

