SIEA Flap
SIEA Flap Breast Reconstruction
Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap
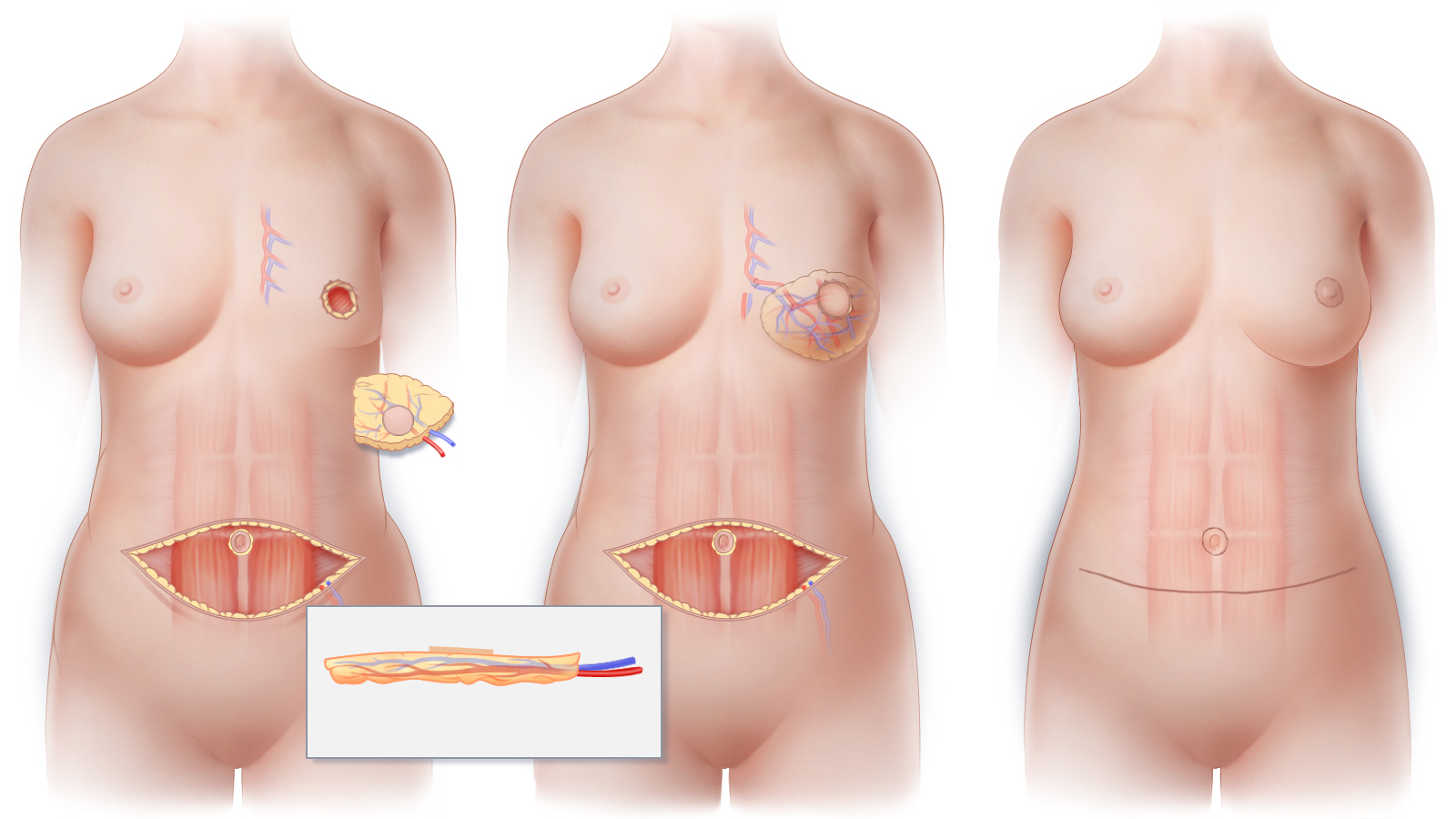
(A) The superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) and the superficial inferior epigastric vein (SIEV) are the blood supply for the skin and fat of an SIEA perforator flap. These vessels travel in the fatty tissue just below the skin. (Inset) Cross-sectional view shows the SIEA and SIEV as they enter the flap directly. (B) The SIEA flap is transferred to the chest; using microsurgical techniques, the SIEA and SIEV are connected to blood vessels at the recipient site in order to restore circulation to the newly reconstructed breast. (C) The horizontal abdominal scar that results following SIEA flap surgery is similar to that created by a “tummy tuck” while the scar that results on the breast will depend on the technique used for mastectomy.

(A) The superficial inferior epigastric artery (SIEA) and the superficial inferior epigastric vein (SIEV) are the blood supply for the skin and fat of an SIEA perforator flap. These vessels travel in the fatty tissue just below the skin. (Inset) Cross-sectional view shows the SIEA and SIEV as they enter the flap directly. (B) The SIEA flap is transferred to the chest; using microsurgical techniques, the SIEA and SIEV are connected to blood vessels at the recipient site in order to restore circulation to the newly reconstructed breast. (C) The horizontal abdominal scar that results following SIEA flap surgery is similar to that created by a “tummy tuck” while the scar that results on the breast will depend on the technique used for mastectomy.
From a patient’s perspective, the DIEP and SIEA flaps are essentially indistinguishable.
Much like the DIEP flap, the SIEA flap employs the skin and fat of the lower abdominal area for breast reconstruction. After the incision is made for a lower abdominal perforator flap, the superficial inferior epigastric artery and vein are visible immediately beneath the skin. These vessels supply the skin and soft tissue of the abdomen and do not pass through the rectus abdominis muscle. In about 10% of women, these vessels are large enough to nourish the tissue needed for the breast reconstruction, and an SIEA flap can be performed.
As is the case for all perforator flaps used in breast reconstruction, no muscle is sacrificed with this procedure. After the tissue is transferred, blood vessels of the flap are connected to vessels at the mastectomy site using microsurgical techniques after which, the tissue of the SIEA flap is then sculpted into a new breast.
Abdominal Contouring
Because the tissue harvested from the abdomen during an SIEA is akin to that removed during a tummy-tuck, women who undergo this procedure generally benefit from an improvement in the contour of their abdomen. Since the scar on the lower abdomen that results from harvest of an SIEA flap is similar to that of a tummy-tuck, it can typically be concealed in most clothing.
Optimizing Aesthetics
Approximately three months after the initial stage of breast reconstruction surgery, reconstruction of your nipples (when mastectomy includes their removal), refinement of breast shape and procedures to produce symmetry with your untreated breast can be completed. These optional additional procedures are performed on an outpatient basis and are referred to as Stage II.
SIEA Flap Surgery in New York and Connecticut
Contact us if you would like more information about SIEA flap breast reconstruction or for information about other options for breast reconstruction after mastectomy including DIEP flaps. Our practice has offices in New York City and Fairfield County, Connecticut.

